Implement Content Provider in Android
Hey everyone!
As developers, we often need to create applications that can share data with other applications residing on the Android device. A content provider is similar to a database where one can query it, edit its content, as well as add or delete content using insert, update, delete, and query methods.
As mentioned on the developer's page, Content providers manage access to a structured set of data. They encapsulate the data, and provide mechanisms for defining data security. In this tutorial, we will learn how to implement a Content provider in Android.
Pre-requisites: Eclipse IDE, Android SDK
Step 1: Create Android project
Launch Eclipse IDE and create a new Android application project called AndroidContentProviderExample with package name com.app.myprovider and choose the target SDK as Android 4.4
Step 2: Create ContentProvider class
Let's write our own ContentProvider that will enable users to add a particular name in the Student table of the College database. Create a new class called MyProvider and write the following code!
MyProvider.java
package com.app.myprovider;
import java.util.HashMap;
import android.content.ContentProvider;
import android.content.ContentUris;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.UriMatcher;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.SQLException;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteQueryBuilder;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyProvider extends ContentProvider {
public static final String PROVIDER_NAME = "com.app.provider.Names";
public static final String URL = "content://" + PROVIDER_NAME + "/names";
public static final Uri CONTENT_URI = Uri.parse(URL);
public static final String NAME = "name";
public static final String ID = "id";
private static HashMap<String, String> namesMap;
//database variables
DBHelper dbHelper;
private SQLiteDatabase database;
static final String DATABASE_NAME = "College";
static final String TABLE_NAME = "Student";
static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 1;
static final String CREATE_TABLE =
" CREATE TABLE " + TABLE_NAME +
" (id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, " +
" name TEXT NOT NULL);";
// integer values used in content URI
static final int NAMES = 1;
static final int NAMES_ID = 2;
static final UriMatcher uriMatcher;
static{
uriMatcher = new UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH);
uriMatcher.addURI(PROVIDER_NAME, "names", NAMES);
uriMatcher.addURI(PROVIDER_NAME, "names/#", NAMES_ID);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Context context = getContext();
dbHelper = new DBHelper(context);
// permissions to be writable
database = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
if(database == null)
return false;
else
return true;
}
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection,
String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SQLiteQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new SQLiteQueryBuilder();
queryBuilder.setTables(TABLE_NAME);
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)) {
// maps all database column names
case NAMES:
queryBuilder.setProjectionMap(namesMap);
break;
case NAMES_ID:
queryBuilder.appendWhere( ID + "=" + uri.getLastPathSegment());
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI " + uri);
}
if (sortOrder == null || sortOrder == ""){
sortOrder = NAME;
}
Cursor cursor = queryBuilder.query(database, projection, selection,
selectionArgs, null, null, sortOrder);
cursor.setNotificationUri(getContext().getContentResolver(), uri);
return cursor;
}
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
long row = database.insert(TABLE_NAME, "", values);
// If record is added successfully
if(row > 0) {
Uri newUri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(CONTENT_URI, row);
getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(newUri, null);
return newUri;
}
throw new SQLException("Fail to add a new record into " + uri);
}
@Override
public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int count = 0;
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case NAMES:
// delete all the records of the table
count = database.delete(TABLE_NAME, selection, selectionArgs);
break;
case NAMES_ID:
//gets the id
String id = uri.getLastPathSegment();
count = database.delete( TABLE_NAME, ID + " = " + id +
(!TextUtils.isEmpty(selection) ? " AND (" +
selection + ')' : ""), selectionArgs);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported URI " + uri);
}
getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null);
return count;
}
@Override
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection,
String[] selectionArgs) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
private static class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
public DBHelper(Context context) {
super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
db.execSQL(CREATE_TABLE);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.w(DBHelper.class.getName(),
"Upgrading database");
db.execSQL("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS " + TABLE_NAME);
onCreate(db);
}
}
}
Step 3: Create Activity class
Next, let's create our Activity class called MainActivity that will allow user to add, delete or show the respective values.
MainActivity.java
package com.app.myprovider;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
//delete all the records and the table of the database provider
public void deleteAllNames(View view) {
String URL = "content://com.app.provider.Names/names";
Uri friends = Uri.parse(URL);
int count = getContentResolver().delete(
friends, null, null);
String countNum = "App: "+ count +" records are deleted.";
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(),
countNum, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
//add a new name
public void addName(View view) {
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(MyProvider.NAME,
((EditText)findViewById(R.id.name)).getText().toString());
Uri uri = getContentResolver().insert(
MyProvider.CONTENT_URI, values);
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(),
"App:" + uri.toString() + " inserted!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
//display all names
public void showAllNames(View view) {
String URL = "content://com.app.provider.Names/names";
Uri friends = Uri.parse(URL);
Cursor c = getContentResolver().query(friends, null, null, null, "name");
String result = "App Results:";
if (!c.moveToFirst()) {
Toast.makeText(this, result+" no content yet!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}else{
do{
result = result + "\n" + c.getString(c.getColumnIndex(MyProvider.NAME));
} while (c.moveToNext());
Toast.makeText(this, result, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="${relativePackage}.${activityClass}" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="@string/name" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnAdd"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/name"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:onClick="addName"
android:text="@string/add" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnShow"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/btnAdd"
android:layout_below="@+id/btnAdd"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:onClick="showAllNames"
android:text="@string/show" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnDelete"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/btnShow"
android:layout_below="@+id/btnShow"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:onClick="deleteAllNames"
android:text="@string/delete" />
</RelativeLayout>
strings.xml
<string name="name">Name</string>
<string name="add">Add a new name</string>
<string name="show">Show all names</string>
<string name="delete">Delete all names</string>
Step 4: Register Provider in Manifest file
Further, for Android to use our provider it is important to register the same in the AndroidManifest.xml as follows!
AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.app.myprovider"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="19" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<provider
android:name=".MyProvider"
android:authorities="com.app.provider.Names" >
</provider>
</application>
</manifest>
Finally, make sure no errors are present. Run the application on an Android device and you should be able to insert, delete and display the list of names as follows! 😄
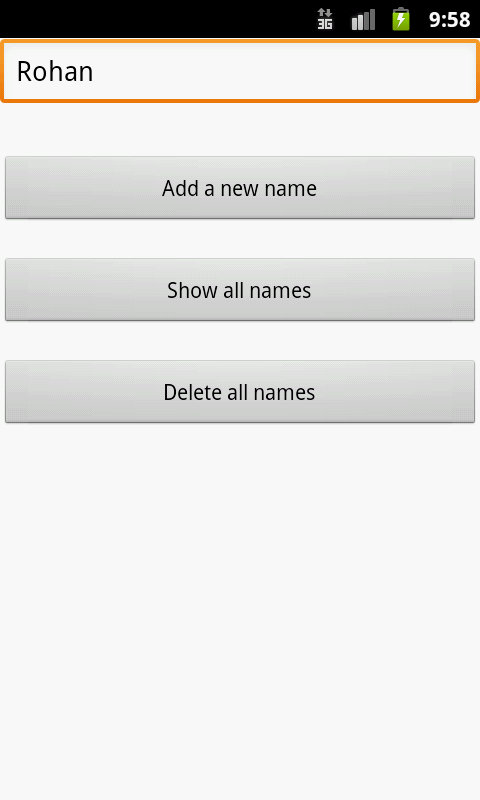
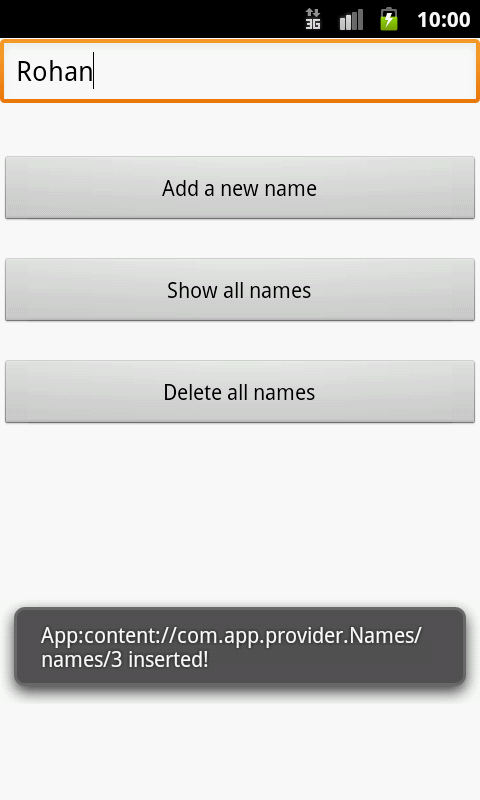
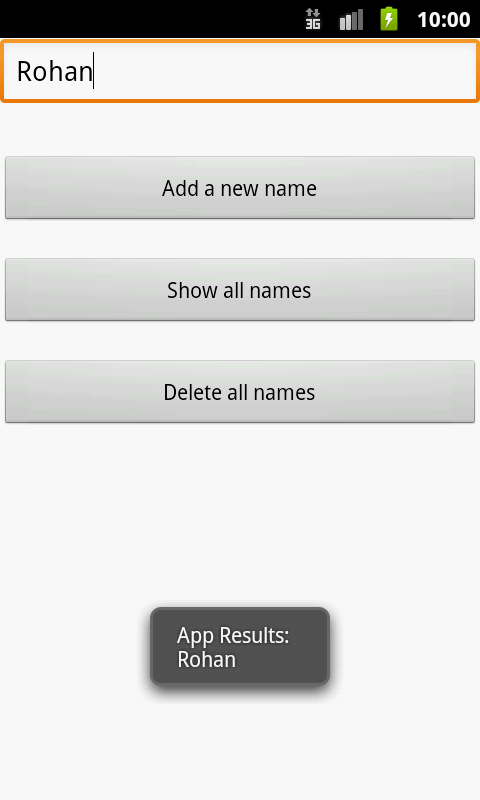
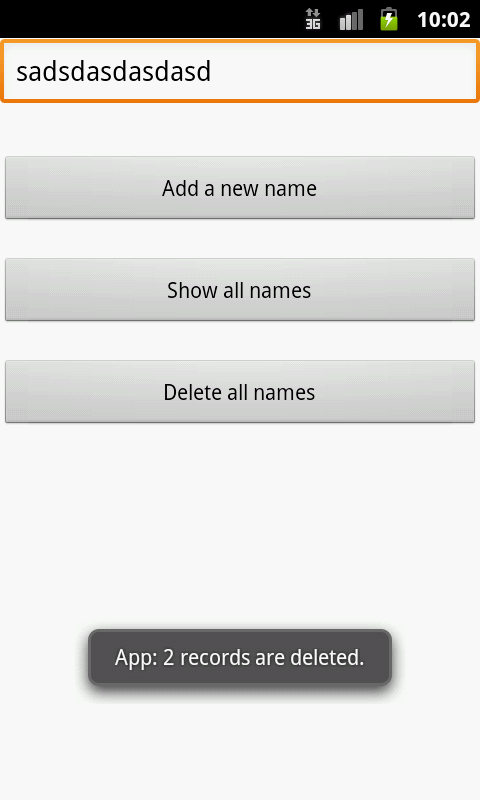
Reference: Android Content Providers
